How to spread bet on forex: a comprehensive guide
Understanding both the benefits and the risks, and how to manage them, is crucial for anyone looking to spread bet on forex.

Written by: Ioan Smith | Expert Financial Writer
Understanding spread betting on forex
What is forex spread betting?
Forex spread betting is speculating on the price movements of currency pairs. Instead of buying or selling the currencies directly, you place a bet on whether the price of a currency pair will rise or fall. You stake a set amount per point (pip) of price movement, enabling you to profit from fluctuations in the forex market. As a leveraged product, spread betting can increase your exposure – which can magnify your profits, but also your losses.
Key advantages and risks of spread betting on forex
Advantages
- Tax-free profits:1 spread betting profits are typically exempt from capital gains tax and stamp duty in the UK and Ireland.
- Leverage: you can control a large position with a small initial deposit (margin), potentially amplifying profits.
- Ability to go long or short – you can profit from both rising (buying) and falling (selling) currency prices.
- Tight spreads – as the forex market is highly liquid and major pairs are often low in volatility, brokers can provide some of their best spreads
- 24-hour market – the forex market operates 24/5, offering trading opportunities around the clock.
- Fast execution – the high number of buyers and sells means fast trade execution with minimal slippage in normal market conditions.
- Risk-management tools – features like stop-loss and limit orders help manage risk effectively.
Risks
- Leverage – while leverage can magnify gains, it can also lead to substantial losses, potentially exceeding your initial deposit.
- Market volatility – forex markets can become highly volatile, leading to rapid price swings that may trigger stop losses or margin calls.
- Wider spreads in volatile markets – brokers may widen spreads during major news events, increasing the cost of trading.
- Psychological pressure – the fast-paced nature of forex trading can lead to emotional decision-making, increasing the risk of losses.
- Overtrading temptation – since forex markets are always active, traders may overtrade, leading to excessive risk exposure.
1The term ‘tax-free’ refers to current UK tax law, which states that UK spread betting profits are exempt from capital gains tax. Please be aware that tax treatment depends on your individual circumstances and tax law may be subject to change. It is recommended to consult a tax professional for personal advice.
How does liquidity affect spread betting on forex?
Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price. In the forex market, high liquidity means there is a large volume of buyers and sellers, and prices move more smoothly.
- High liquidity:
•Major forex pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY tend to have high liquidity because they are actively traded globally. High liquidity typically results in tighter spreads (lower costs) and less slippage (the difference between the expected price and the actual price of the trade).
- Low liquidity:
•Exotic currency pairs or less-frequently traded pairs may have lower liquidity, leading to wider spreads and slippage. This increases your costs and can make execution slower or more volatile.
How does volatility affect spread betting on forex?
Volatility refers to the degree of price movement within a specific time frame. It is a critical factor in forex spread betting because it directly impacts your potential profits and losses. Here’s how volatility affects your trades:
- Increased profit potential: Higher volatility means larger price swings, which can lead to larger profits if you are positioned correctly. For example, during volatile market conditions, if you're in a long position and the currency pair moves favourably, the potential to profit per pip is greater.
- Increased risk: While volatility can lead to higher profits, it also amplifies the risk. In volatile conditions, the market can move unpredictably, making it harder to predict the direction. If the market moves against your position, you could incur significant losses.
Managing volatility:
- Use stop-loss orders to protect against sharp price reversals.
- Consider reducing your stake size during highly volatile periods to manage risk.
- Be aware of economic events or geopolitical factors that may cause market spikes.
What is the difference between going long and going short in forex spread betting?
In forex spread betting, going long and going short refer to betting on the price direction of a currency pair:
- Going long: You take a buy position when you expect the price of a currency pair to rise. If the price increases, you make a profit, while a price decrease results in a loss.
- Going short: You take a sell position when you believe the price of a currency pair will fall. If the price declines, you earn a profit, but if it rises, your position incurs a loss.
How is spread betting taxed compared to other forms of forex trading?
For UK traders, spread betting can be a tax-efficient option because profits are tax-free.1 However, CFD trading and spot forex allow loss offsetting for tax purposes, which may be beneficial for some traders. This table summarises the tax differences between spread betting, CFD trading, and spot forex trading in the UK:
| Spread betting | CFD trading | Spot forex trading | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital gains tax (CGT) | ❌ No CGT | ✅ Yes (up to 20%) | ✅ Yes (if considered an investment) |
| Income tax | ❌ No (unless a primary income source) | ✅ Yes (if trading as self-employed) | ✅ Yes (if trading as self-employed) |
| Stamp duty | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Loss offset | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (can offset against gains) | ✅ Yes (can offset against gains) |
| Regulatory classification | Gambling | Investment/trading | Investment/trading |
1The term ‘tax-free’ refers to current UK tax law, which states that UK spread betting profits are exempt from capital gains tax. Please be aware that tax treatment depends on your individual circumstances and tax law may be subject to change. It is recommended to consult a tax professional for personal advice.
Getting started with forex spread betting
Opening a spread betting account
To start spread betting on forex you need to consider the following steps:
- Select a broker: Choose a regulated broker such as Pepperstone to ensure stringent compliance and security standards. Other factors to look out for include low fees, fast execution, risk-management tools, reliable platforms, third-party integrations, and good customer support.
- Apply for an account: You’ll be asked to answer some questions to check your suitability to the products, and then complete an ID check to verify your identity. The whole process normally takes just a few minutes.
- Deposit funds: The minimum deposit varies by broker, but for Pepperstone it is just £10.
Which forex pairs are most suitable for spread betting?
When choosing forex pairs for spread betting, traders typically look for high liquidity, tight spreads, and volatility to maximise potential profits while managing risk. Here are some forex pairs to consider when spread betting:
Major currency pairs (tight spreads & high liquidity)
Major pairs are highly liquid, meaning they tend to offer the tightest spreads when spread betting. Some examples include:
Minor pairs
These pairs don’t include the USD but can be more volatile, offering the potential for greater movement:
- EUR/GBP
- EUR/JPY
- GBP/JPY
- AUD/JPY
Exotic pairs
Exotic pairs involve currencies from emerging markets and usually have wider spreads and higher volatility. Some examples include:
- USD/TRY (Turkish Lira)
- USD/ZAR (South African Rand)
- USD/MXN (Mexican Peso)
Mechanics of trading
How do I place a spread bet on a forex pair?
Placing a spread bet on a forex pair generally follows these steps:
- Choose an FX pair to trade: Select the currency pair you want to trade, such as GBP/USD, EUR/USD, or USD/JPY.
- Decide your position: You can go long (buy) or go short (sell) based on which way you think the price will move.
- Set your bet size: Determine how much you are willing to stake per pip. Remember your stake size will be multiplied by the number of pips the price moves to calculate your profit or loss.
- Set stop-loss and take-profit orders: A stop-loss can help cap your losses by automatically closing your position if the market moves too far against you. A take-profit can lock in profits by closing your position at a specified level if the market moves in your favour.*
*Note in fast-moving or volatile markets, slippage may occur. This means your position may not be closed at the exact price set, and the execution price could be less favourable than expected. Therefore stops and limits can assist in managing your trading strategy, but they do not guarantee specific outcomes.
How do bid-ask spreads impact trades?
The bid-ask spread represents the difference between the bid price (sell) and the ask price (buy). It plays a significant role in forex spread betting, affecting both your entry and exit points:
- Bid price: The price at which you can sell the currency pair.
- Ask price: The price at which you can buy the currency pair.
In spread betting, the broker normally wraps a spread around the market price, which is their fee for facilitating the trade. The spread cost is factored in from the start, so you’ll enter the trade at a slight loss and will need to move through the market price before you start turning a profit. The wider the spread, the more the market must move in your favour before you can start earning.
Example:
- Bid price: 1.2600
- Ask price: 1.2602
- The spread here is 2 pips. If you buy, you will need the market to move 2 pips in your favour before you break even.
The tighter the spread, the lower the cost of entering and exiting trades, making it a key factor in forex spread betting. High-volume traders and scalpers might want to consider opening a Razor account with Pepperstone, which offers raw spreads from 0.0 points, alongside fixed, transparent commissions from £2.25 per lot, per side.
Leverage and margin in spread betting
In spread betting, leverage and margin are essential concepts that determine how much capital you need to control larger positions in the market. The regulator allows leverage up to 30:1 on forex spread bets, meaning you can control positions that are 30 times larger than your initial deposit. This means that both profits and losses are significantly amplified, as they’re based on the full value of your position.
- Leverage: This is essentially the multiplier between the deposit required and your full exposure. So with 30:1 leverage, you can control a position worth £30,000 with just £1,000 of your own capital.
- Margin: This is the capital required to open and maintain a leveraged trade. There are two main types:
• Deposit (initial) margin: The amount needed to open a position. So in the example above, the £1000 you put down would be your initial margin.
• Maintenance margin: Additional funds that may be required to keep the position open if the market moves unfavourably. If your trade moves against you and your margin drops below the threshold required by your broker, you may receive a margin call to deposit more funds.
Understanding how leverage and margin work is essential when spread betting. Always use leverage wisely and ensure you have sufficient margin to protect your positions from unexpected closure.
Spread betting example: GBP/USD with 30:1 leverage
You expect GBP to strengthen against USD and place a £2 per point bet at 1.3000, with leverage of 30:1.
Position size & margin calculation:
- Notional value: £20,000. This is because the standard lot size for GBP/USD is 10,000, and you’ve bet £2 per point of movement.
- Margin required: £666.66 (£20,000 ÷ 30).
In spread betting, your gains or losses depend on the difference between the entry and closing price, multiplied by your stake per pip.
If GBP/USD rises to 1.3100, the move is 100 pips. Your profit will therefore be 100 x £2 = £200.
If GBP/USD instead drops to 1.2900, the move is 100 pips. Your loss will therefore be 100 × £2 = £200.
Types of spread bets
Unlike some traditional investments with set timeframes, spread bets offer the flexibility to be closed at any time during trading hours. The duration of your bet largely depends on the type chosen.
Spread bets fall into two main categories based on how long you plan to hold your position:
- Cash bets: These are short-term positions, often settled by the end of the trading day. Your profit or loss is determined by the difference between the asset’s entry and exit prices when you close the position. This type of spread bet offers the tightest spreads, but you’ll pay a small fee for holding the position overnight.
- Forward bets: These are longer-term trades, where you bet on an asset’s price movement over weeks or even months. The price is locked in when you place the bet, and the trade settles on a predetermined future date. You’ll pay a wider spread than with a cash bet, but you won’t pay any funding charges for holding your position overnight.
Overnight financing costs in spread betting
Overnight financing costs, also known as rollover fees or swap rates, apply when you hold a cash position open overnight. These costs are influenced by the interest rate differential between the two currencies in a pair and can either be positive or negative, depending on the direction of your trade. The rate is based on the interbank lending rates (eg LIBOR, SOFR) plus the broker’s fee.
How to manage financing costs:
- Check the swap rates: Make sure to check the overnight financing rates for your chosen currency pair before holding positions overnight.
- Plan your trades: If you're trading short-term, you can avoid overnight fees by closing positions before the trading day ends.
- Consider the long-term impact: If you plan on holding positions for extended periods, be mindful of how financing costs might erode your profits or amplify your losses.
How to manage your risk when spread betting on forex
What are the most effective risk management techniques for spread betting on forex?
Effective risk management is crucial when spread betting on forex due to the volatility of currency markets. Some key techniques include:
- Position sizing: Limit the size of your trades based on your risk tolerance. Some traders avoid risking more than 1-2% of their trading capital on any single trade.
- Setting stop-loss orders: These can automatically close your position if the market moves against you by a predetermined amount, limiting potential losses.
- Risk-to-reward ratio: Aim for a favourable risk-to-reward ratio, ensuring that the potential reward justifies the risk of the trade.
- Diversification: Avoid concentrating all your trades in a single currency pair. Spread your risk by diversifying across multiple pairs or different types of trades.
- Market alerts: Notifications to track price movements and identify trading opportunities. These can be received into the trading platform or often to your mobile device.
- Ongoing education: Access to market analysis, educational tools, and trading resources to improve decision-making.
Retail spread bettors have negative balance protection, which means that the money on their account cannot fall below zero. This is a regulatory requirement and must be met by your broker.
How do I use stop-loss and limit orders effectively in spread betting?
Stop-loss and limit orders are essential tools to manage risk in forex spread betting:
- Stop-loss orders: Set a stop-loss to automatically exit your position if the market moves against you by a certain number of pips. This helps protect your capital and prevents larger-than-expected losses. Example: If you’re trading GBP/USD at 1.2600, you might set a stop-loss at 1.2550 to limit a loss to 50 pips.
- Limit orders: A limit order locks in your profit by closing your position at a predetermined level once the price reaches a specific target. This is useful for locking in gains without needing to monitor the market constantly. Example: If you’ve entered a buy trade at 1.2600, you might set a limit order at 1.2650 to lock in a 50-pip profit.
What is slippage, and how can it impact my forex spread bets?
Slippage occurs when the price at which your trade or order is executed is different from the price you expected. This can happen during periods of high volatility, such as news announcements or major market events. Slippage can affect both your entry price and your exit price, and can be both negative or positive.
Are there specific strategies that work well for forex spread betting?
Each strategy has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best one for you will depend on your trading style, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Combining different strategies, such as using trend-following for long-term trades and range trading for short-term setups, can also be effective in forex spread betting. Regardless of your strategy, always ensure that you employ proper risk-management techniques (such as setting stop-loss and take-profit orders) to protect your capital.
- Trend following: This strategy involves identifying and trading in the direction of the prevailing market trend. Traders use technical indicators like moving averages or trendlines to spot trends and enter trades in the direction of the trend. The idea is to capitalise on sustained price movements in one direction.
Example: If GBP/USD has been steadily rising, you might open a long position, betting that the price will continue to rise. - Mean reversion: This strategy assumes that prices will eventually revert to their mean or average level after straying too far in one direction. Traders using this strategy might enter a position when a currency pair’s price moves significantly away from its historical average, anticipating that the price will eventually return to that level.
Example: If GBP/USD rises significantly above its average price, you might short the pair, expecting the price to fall back to its mean. - Breakout trading: Breakout trading involves entering a trade when the price breaks through a key support or resistance level, signalling the start of a new trend. This strategy relies on the idea that once the price breaks out, it will continue to move in the breakout direction, either upwards or downwards. Traders typically use technical analysis tools, like chart patterns or indicators, to identify these key levels and place trades when the price breaks them.
Example: If GBP/USD is trading in a range between 1.2500 and 1.2600 and the price breaks above 1.2600, a trader might go long, expecting the price to continue rising. - Range trading: Range trading is based on the idea that prices will tend to fluctuate within a defined range for a period. Traders use support and resistance levels to identify entry and exit points. The strategy involves buying near support and selling near resistance, expecting the price to stay within the established range.
Example: If GBP/USD is trading between 1.2450 and 1.2550, you might buy at 1.2450 (support) and sell at 1.2550 (resistance), betting that the price will remain within the range. - Scalping: Scalping involves making numerous small trades with the goal of profiting from tiny price movements. The idea is to take advantage of small fluctuations in the forex market, usually by holding positions for a very short time. This requires a lot of focus and quick decision-making.
Example: A trader might buy GBP/USD at 1.2570 and sell it minutes later at 1.2575, capturing a 5-pip movement. - News trading: News trading is based on the idea that significant economic news releases can cause sharp price movements in currency pairs. Traders using this strategy try to predict how specific news events (like employment reports, interest rate decisions, or GDP data) will impact a currency and position themselves accordingly. This strategy requires quick reactions and awareness of the market's response to the news.
Example: If a positive employment report for the UK is released, a trader might go long on GBP/USD, expecting the pound to appreciate. - Momentum trading: Momentum trading focuses on entering positions when a currency pair is showing strong momentum in one direction. This strategy relies on technical indicators like the relative strength index (RSI) or moving average convergence divergence (MACD) to identify overbought or oversold conditions, signalling potential continuation or reversal of price movements.
Example: If GBP/USD is showing strong bullish momentum, a trader might buy the pair when the RSI shows it’s not yet overbought, expecting the trend to continue.
Market analysis and execution for forex spread betting
In forex spread betting, both technical and fundamental analysis play important roles in making informed decisions. Here’s how you can approach market analysis and execute trades effectively:
What are the best technical indicators for forex spread betting?
Several technical indicators are popular among forex traders for identifying trends, entry points, and potential reversals. The most effective ones for forex spread betting include:
- Moving averages (MA): Moving averages help smooth out price data to identify trends over a specific period. Simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA) are commonly used to spot bullish or bearish trends.
Example: If the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, it could indicate a buying opportunity (bullish crossover).
_and_SMA_200_(red)_with_buysell_indicators_and_current_price_displayed.jpg)
- Relative strength index (RSI): RSI measures the strength of price movements and identifies overbought or oversold conditions. RSI values range from 0 to 100, with readings above 70 indicating overbought conditions and below 30 indicating oversold conditions.
Example: If GBP/USD shows an RSI reading of 80, it could be considered overbought, suggesting a potential reversal.
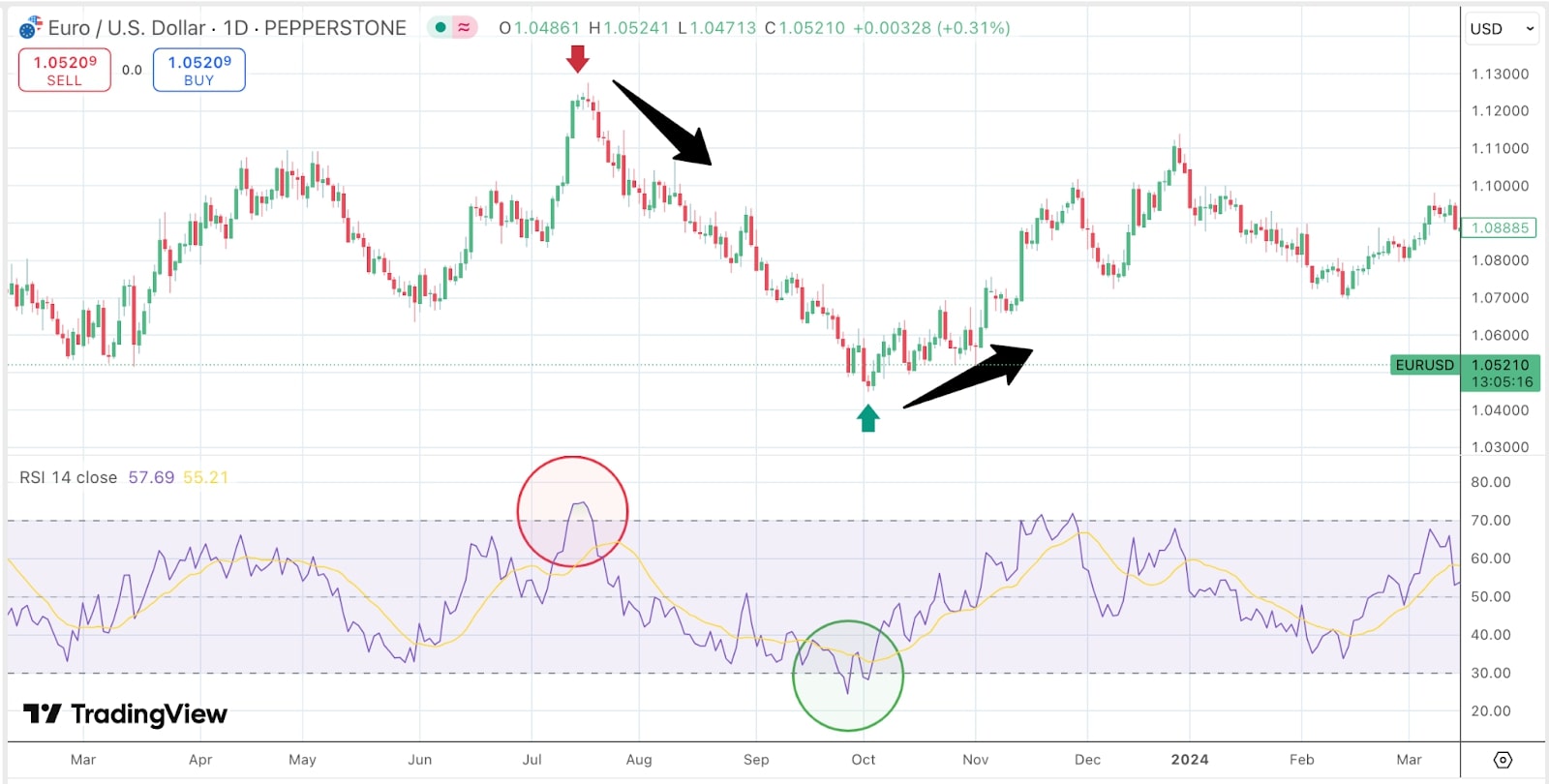
- MACD (moving average convergence divergence): The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a currency pair's price. Traders look for MACD crossovers or divergence from the price to spot potential trend reversals.
Example: A MACD crossover above the signal line may indicate a buy signal for the forex pair. - Bollinger bands: These bands represent volatility and price levels based on standard deviations from a moving average. A price breaking through the upper or lower band could suggest a continuation or reversal, depending on the market conditions.
Example: If GBP/USD price touches the lower Bollinger band and begins to bounce back up, it could signal a buying opportunity.
Can I use fundamental analysis for forex spread betting?
While technical analysis is the most common approach in forex spread betting, fundamental analysis is also highly valuable, especially for those who want to understand the broader economic factors affecting currency prices. The two can be used in combination to create a more comprehensive strategy.
Fundamental analysis focuses on economic indicators, central bank policies, political stability, and other macroeconomic factors to predict the long-term direction of a currency. This type of analysis is especially useful for carry trading or when holding longer-term positions.
Many traders use fundamental analysis to understand the long-term trend of a currency and technical analysis to time their entries and exits. For example, you might use fundamental analysis to determine that the US dollar is likely to strengthen due to expected interest rate hikes and then use technical analysis to identify the right entry point.
How do macroeconomic events impact forex markets?
Macroeconomic events such as interest-rate changes, inflation reports, and employment data significantly impact currency markets. These events can cause increased volatility, offering both opportunities and risks for traders. Key events include:
- Interest-rate decisions: A central bank's decision to raise or lower interest rates directly affects the value of a currency. If the central bank raises rates, the currency typically strengthens as higher interest rates attract foreign investment.
- Inflation reports: Higher-than-expected inflation may lead traders to bet that a central bank will raise rates, thus strengthening the currency. On the other hand, low inflation may suggest a weaker currency.
- Employment data (eg non-farm payrolls): Strong employment data typically supports a currency, as it signals economic health. Weak employment reports may lead to depreciation of the currency.
- Geopolitical events: Political instability or events like elections can cause sharp price movements as traders anticipate the potential effects on economic policies.
How to adjust your bets:
When macroeconomic events are scheduled, it can be a good idea to:
- Stay updated on news releases and economic calendars.
- Use a realistic stop-loss to mitigate risk in volatile conditions.
- Consider using a range-based strategy if you expect uncertainty or lack of clear trends following a news event.
- Monitor reaction to news, as the market might continue moving in a direction after an initial volatile reaction.
What are the best times to spread bet on forex?
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing you to trade at any time. However, certain times of day can be better for spread betting, depending on your trading strategy and goals:
- The London-New York overlap (1-4pm GMT): This is the period when two of the most active forex trading sessions (London and New York) overlap. This period is characterised by higher liquidity and increased volatility, making it suitable for breakout trading and trend-following strategies.
- London session (8am – 4pm GMT): The London session is a highly liquid trading session, with major market movers like the European Central Bank and the Bank of England often making announcements during this period. If you’re interested in trading more stable currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/USD, the London session is a good time.
- Asian session (12-9am GMT): The Asian session, especially early in the morning, is typically quieter and more stable. This can be suitable for range trading or when you want to avoid high volatility.
Can I automate my forex spread betting strategy?
You can automate your forex spread betting strategy through trading algorithms or by using Expert Advisors (EAs) on platforms that support automated trading, like MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5). Here's how automation can benefit your strategy:
- Consistency and discipline: Automated strategies eliminate emotional decision-making, allowing for consistent application of your trading rules. This is particularly useful in momentum trading or scalping, where precision is key.
- Speed: Automation ensures that your trades are executed immediately when your criteria are met. This is particularly beneficial in fast-moving markets or during high volatility.
- Backtesting: Many platforms offer backtesting features, allowing you to test your automated strategy against historical data before applying it to live markets.
While automation is useful, you still need to monitor your trades and adjust your strategies as necessary, especially during major market shifts or economic events.
Choosing a trading platform
Selecting the right trading platform is crucial for efficient forex spread betting. Pepperstone offers a suite of native and third-party tech – including TradingView, MT5 and MT4. Find out more here.
What are common mistakes beginners make when spread betting on forex?
Beginners often make several key mistakes when spread betting on forex that can impact their profitability and risk management:
1. Overleveraging
Using excessive leverage can amplify both profits and losses. Many beginners use high leverage in the hope of bigger profits without fully understanding the risks involved. It's often better to start with low leverage and gradually increase as you gain more experience.
2. Ignoring risk management
Not setting stop-loss and take-profit orders, or failing to use them correctly, can lead to large losses or missed profit opportunities. Always consider placing stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and setting take-profit orders to lock in profits when a position reaches your target.
3. Lack of a clear strategy
Many beginners trade without a defined strategy, relying on impulse or speculation rather than following a systematic approach. It can be useful to develop a clear trading plan based on technical analysis, market conditions, and risk management, to avoid emotional decision-making.
4. Trading without proper knowledge
Jumping into forex spread betting without understanding how it works, or the fundamentals of forex markets is a common mistake. Do take the time to educate yourself on forex market mechanics, trading strategies, and risk-management techniques before starting.
5. Not accounting for market volatility
Ignoring the effects of volatility, especially during major news events or market open/close times, can result in unexpected price movements. Be aware of economic calendars and the potential for increased volatility. Adjust your position sizes and stop-loss limits accordingly.
Further reading
To enhance your understanding of forex spread betting, consider these in-depth guides:
- What is spread betting? – A breakdown of spread betting, how it works, and its advantages.
- What is forex trading? – An introduction to the forex market, key trading concepts, and price influences.
These resources can provide even insights to support your trading. We hope you’ve found this guide use
The material provided here has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research and as such is considered to be a marketing communication. Whilst it is not subject to any prohibition on dealing ahead of the dissemination of investment research we will not seek to take any advantage before providing it to our clients.
Pepperstone doesn’t represent that the material provided here is accurate, current or complete, and therefore shouldn’t be relied upon as such. The information, whether from a third party or not, isn’t to be considered as a recommendation; or an offer to buy or sell; or the solicitation of an offer to buy or sell any security, financial product or instrument; or to participate in any particular trading strategy. It does not take into account readers’ financial situation or investment objectives. We advise any readers of this content to seek their own advice. Without the approval of Pepperstone, reproduction or redistribution of this information isn’t permitted.