Preview For The March 2024 US Jobs Report

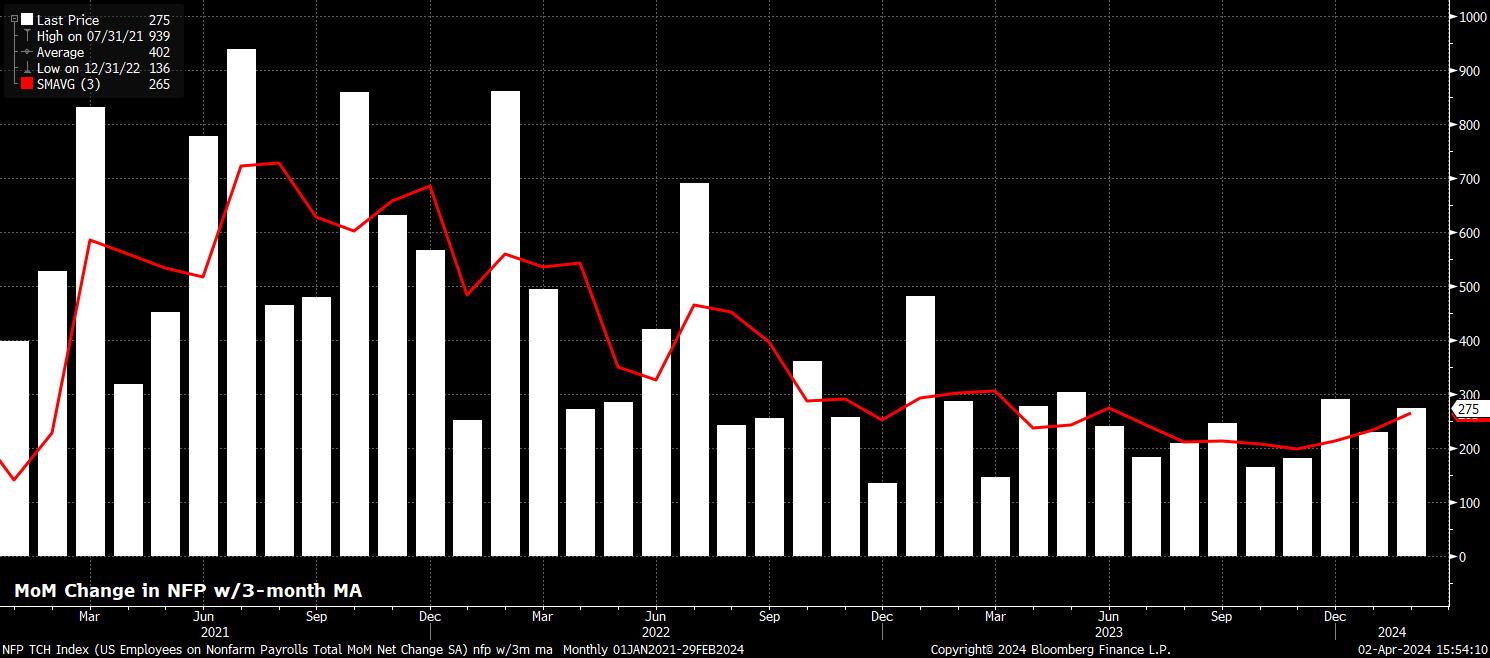
Headline nonfarm payrolls are expected to have risen by +215k last month, a modest slowdown from the +275k pace seen in February, and a pace that would be marginally below the approx. 250k monthly ‘breakeven’ rate of payrolls gains, i.e. the pace required for job growth to keep up with natural growth in the size of the labour force. In any case, pending revisions, a print in line with consensus would see the 3-month average of job gains dip slightly to +240k, from the present +265k, an 8-month high.
Leading indicators for the payrolls print point to few significant downside risks to the consensus NFP estimate.
While the ISM services survey, at the time of writing, is yet to be released, the employment sub-index of the March ISM manufacturing report rose to a YTD high, albeit remaining below the 50.0 boundary which divides expansion and contraction. Meanwhile, both initial and continuing jobless claims were broadly unchanged in the survey week, both compared to the week prior, and – as near as makes no difference – compared to the February survey week. As always, the ADP employment report should be entirely ignored, with the data increasingly bearing no relation at all to the BLS private employment data, with the two in fact being negatively correlated of late.
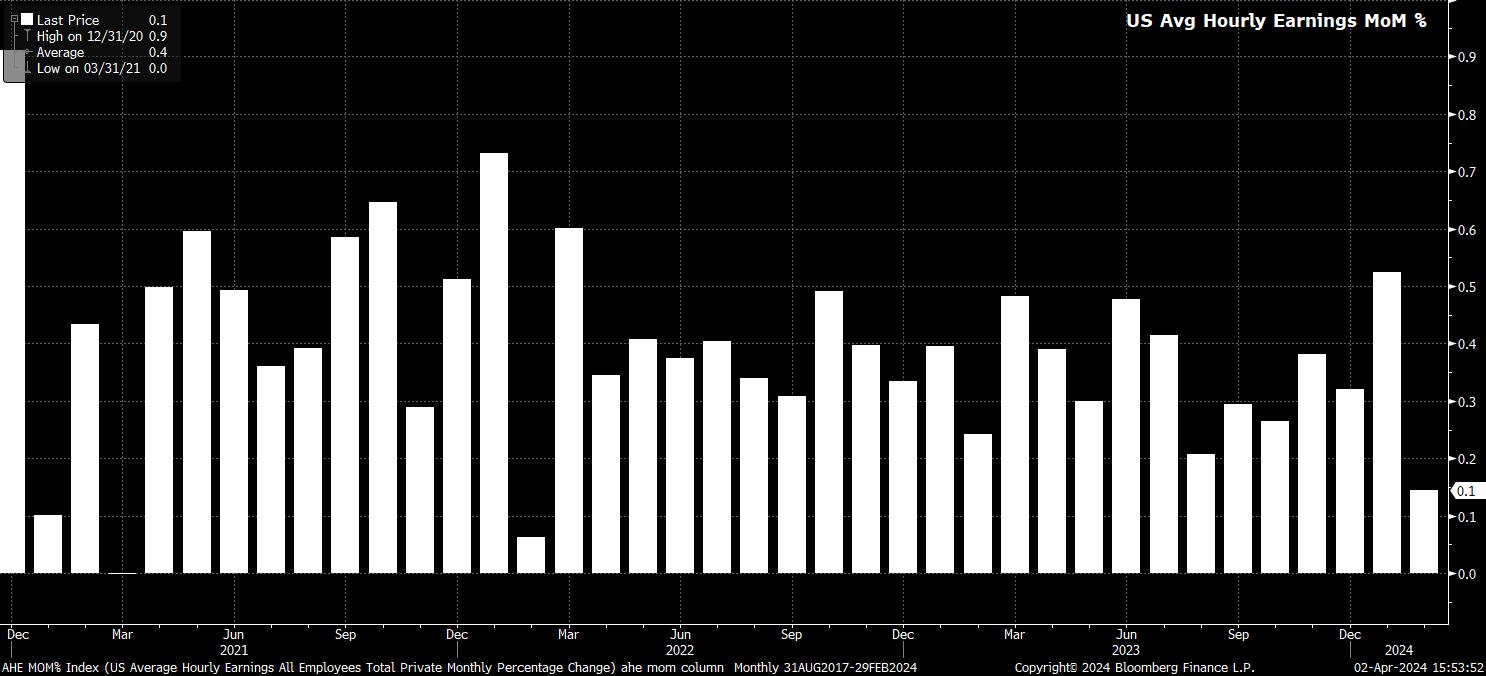
Sticking with the establishment survey, average hourly earnings are set to have risen 0.3% MoM, a modest uptick from the 0.1% MoM pace seen in February, and broadly in line with the pace seen during much of this cycle. On an annual basis, this would see earnings growth fall to around 4.1% YoY, though this would likely still represent >1% annual real earnings growth, pending the release of March CPI next week.
Of course, FOMC members will be seeking a rather significant cooling in earnings pressures, particularly as services prices remain stubbornly high. A more rapid pace of services disinflation is likely to be necessary over coming months as the deflationary impulse from goods begins to fade, in order to provide the required “confidence” that inflation is returning towards the 2% target, thereby allowing policy normalisation to begin.
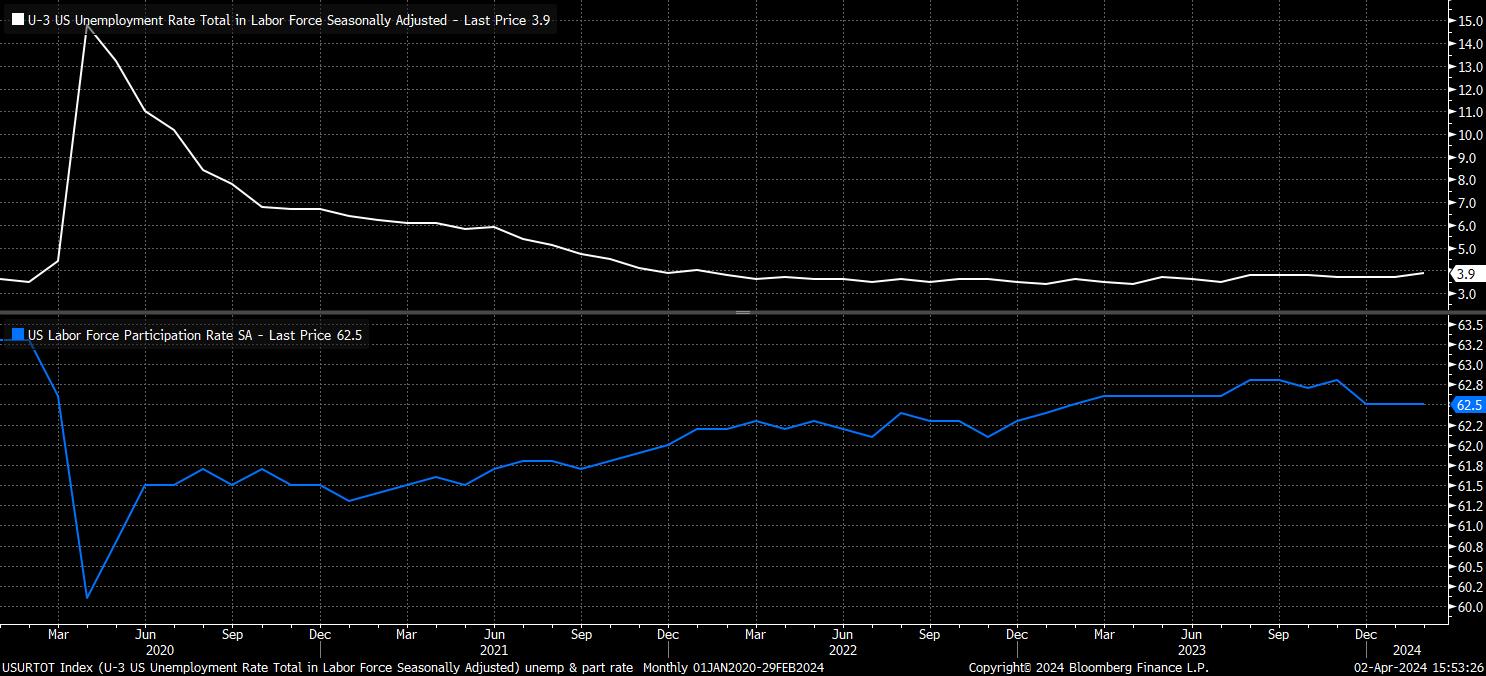
Meanwhile, turning to the household survey, unemployment is expected to tick down to 3.8%, a pullback from the 3.9% seen in February, which was the highest headline unemployment rate seen since January 2022. Participation, however, is set to remain at 62.5%, a level from which the rate has not budged since the apparently weather-related decline at the start of the year.
Nevertheless, context is key here, with both of those metrics – albeit marginally away from the best levels of this cycle – continuing to signify a jobs market that remains at, or close to, full employment. Furthermore, with the median end-24 unemployment forecast in the March SEP sitting at 4.0%, a further modest weakening of the labour market is to be expected, and in itself is unlikely to elicit a strong policy response.
Putting all of this together will provide the latest catalyst in the ongoing market debate over whether this year will bring 75bp, as signalled in the March dots, or 50bp of cuts from the FOMC. At the time of writing, markets are rather delicately poised, pricing a roughly even chance of either outcome, with the hawks having been spurred on by hotter-than-expected ISM manufacturing figures.
The equation here is a relatively simple one, with hotter-than-expected figures likely to ignite a knee-jerk hawkish cross-asset reaction, and the opposite true of a cooler-than-expected report. Unemployment, and average earnings, are likely of more significance than the headline payrolls print, though in any case dips in risk are likely to be relatively short-lived, with the policy outlook remaining supportive, and the ‘Fed put’ well and truly alive once more.
In addition, despite risks to the dual mandate clearly coming into better balance, the inflation side of said mandate remains the most significant in determining both the timing, and the pace, of policy normalisation, barring any “unexpected” weakening of the jobs market, or potential financial accident to which policymakers would be forced to respond.
Bearing this in mind, at least in terms of sustained market reaction, the March CPI report, due 10th April, is likely to be significantly more consequential. This is especially true bearing in mind that headline YoY CPI has been hotter-than-expected for three months running, and as the ‘confidence’ that policymakers need to deliver the first cut of the cycle continues to prove elusive.
Related articles
Pepperstone不代表這裡提供的材料是準確、及時或完整的,因此不應依賴於此。這些資訊,無論來自第三方與否,不應被視為建議;或者買賣的提議;或者購買或出售任何證券、金融產品或工具的招攬;或參與任何特定的交易策略。它不考慮讀者的財務狀況或投資目標。我們建議閱讀此內容的讀者尋求自己的建議。未經Pepperstone的批准,不允許複製或重新分發此信息。